Blind Spots and Blurry Vision
Macular Degeneration is a medical condition which results in vision loss in the center of the visual field (the macula) because of damage to the retina. Macular degeneration can advance to legal blindness and inability to drive. The macula, a paper-thin tissue is located roughly in the center of the retina and at the back of the eye where light sensitive cells send visual signals to the brain. It is temporal to the optic nerve. It is a small and highly sensitive part of the retina responsible for your detailed central vision. Sharp, clear, straight-ahead vision is processed by the macula, and damage to it results in blind spots and blurred or distorted vision. Macular degeneration can occur in either a dry or wet form. The condition mostly occurs in elderly patients and is the leading cause of severe vision loss in people over the age of 60. With macular degeneration, it can be extremely difficulty or impossible to read and distinguish faces, although there seems to be enough peripheral vision remaining to carry out other daily activities.
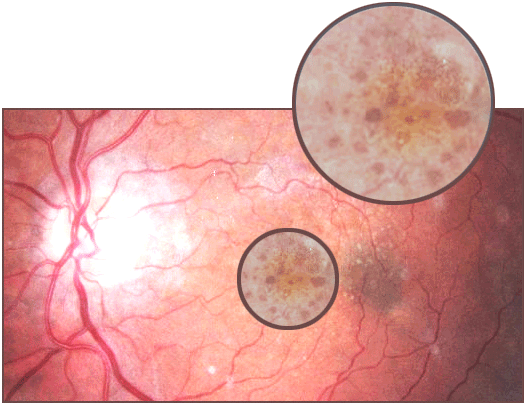
The retina is located in the inner layer of the eye and contains vital nerves that broadcast your sight. In behind the retina is the choroid which supplies blood to the retina. In the the dry form (nonexudative) of Macular Degeneration, cellular debris called drusen can accumulate between the retina and the chroroid, and the retina can become detached. In the wet form (exudative) blood vessels grow from the choroid behind the retina and the retina can also become detated. The wet form of the condition is by far the more severe. It can be treated with laser coagulation, and with medication that stops and sometimes reverses the growth of the blood vessels.
Macular degneration begins usually with characterstic yellow deposits in the the macula, the central area of the retina called the fovea. The yellow deposits are called drusen and they develop between the retinal pigment epithelium and the choroid. Most patients who develop these early characteristics have good vision. However, people with drusen can go on to develop advanced age-related maculopathy or AMD. The risks are much higer with larger and more numerous amounts of drusen. Recent research does suggest that large, soft drusen are related to heightened cholesterol deposits and may be treated with cholesterol lowering agents.
Often, the dry form (exudative) of macular degeneration initially causes slightly blurred central vision, both near and far. The center of vision may become slightly fuzzy or shadowed, and this area grows larger as the disease develops. Blind spots may develop, and it is normally more difficult to see color and fine detail. Commonly, in wet macular degeneration, in addition to the above symptoms, straight lines may appear wavy. Also, in this more severe form, central vision loss can occur rapidly, sometimes within days or weeks. During the early stages of macular degeneration, and if only one eye is affected, there may be no symptoms at all. Additionally, neither form of macular degeneration (dry or wet) causes any sort of pain. However, a retinal specialist may be able to detect early signs of the disease before symptoms appear. Therefore, it is very important to have regular eye examinations to detect these signs as soon as possible.
To help diagnose macular degeneration, an eye care professional or retinal specialist will perform a comprehensive eye exam which may include several of the following tests and diagnosis. The Amsler grid is a test whereby the patient may be asked to look at a grid composed of black, straight lines running horizontally and vertically, and a black dot in the center. For people with macular degeneration who stare at the black dot, the lines on the grid may appear wavy, distorted or disappear completely. A dilated eye exam might be necessary to view the back of the retina. Dilation, which would be administered by using eye drops to dilate the pupils, allows the doctor see the retina more easily to determine any optic nerve damage. An ophthalmoscopy might also be undertaken. This tests is where the pupil is dilated and a bright beam of light is aimed into the eye to view the retina, choroid, blood vessels and optic disk. Fundus photography is where the pupil is dilated, light is focused through the cornea, pupil and lens, and a customized camera photographs at high res the back of the eye, including the retina, macula and optic nerve. Fluorescein angiography might also have to be undertaken if the wet form of macular degeneration is suspected, this test may be done to detect leaking blood vessels. A dye is injected into the arm of the patient, and is traced as it courses through the blood vessels in the retina, where it can reveal leakage.
It is extremely important to have regular eye examinations, particularly as individuals get older, or if you have any of the risk factors associated with Macular Degeneration. If only one eye is affected, as mentioned previously, by macular degeneration, there may be no noticeable symptoms or signs, but a doctor can still make an accurate diagnosis of any conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment may help control progression of the disease, and stabilize or even restore some vision.
For additional information or to schedule a Glaucoma Test, please contact us at (866) 861-3937.
Also Serving:
Sealy, TX - Bellville, TX - Columbus, TX - Katy, TX |
